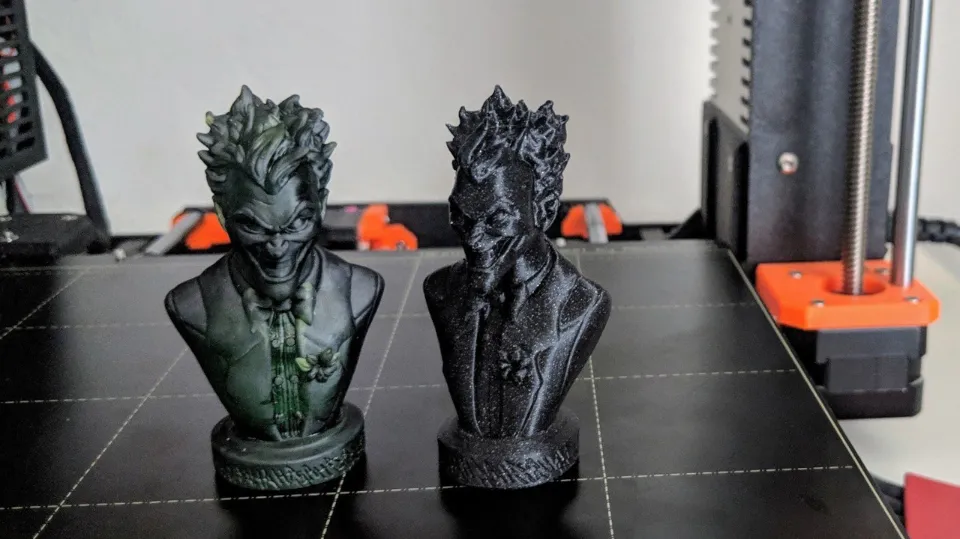

Resin 3D printers have become increasingly popular over the years, with the technology allowing for highly detailed, intricate designs to be created with ease. But how do resin 3D printers work?
The resin 3D printer constructs an object layer by layer until it is complete by exposing a layer of photosensitive liquid resin to a UV-laser beam. The resin hardens in the desired pattern after being exposed to the laser beam.
In this article, we will explore the technology behind these printers and how they produce high-quality 3D prints.
What is a Resin 3D Printer?
A resin 3D printer is a type of additive manufacturing device that uses liquid photopolymer resin to create 3D objects. Unlike Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D printers, which use plastic filament, resin printers use a liquid resin that is cured using a light source. Resin printers are known for their high level of detail and accuracy, making them a popular choice for prototyping and creating complex designs.
How Does a Resin 3D Printer Work?
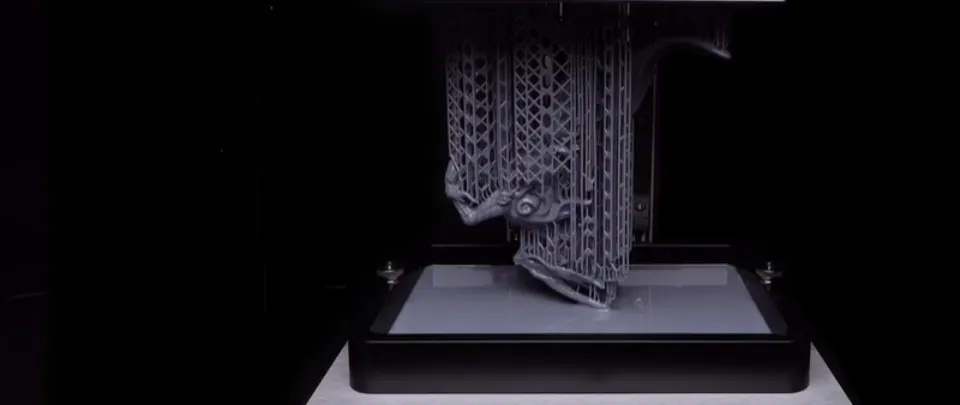
The process of creating a 3D print with a resin printer begins with designing the 3D model using CAD software. Once the design is complete, the file is exported in a format that the printer can read. The printer software then slices the 3D model into thin layers, which are sent to the printer.
The resin printer uses a liquid resin that is stored in a vat at the bottom of the printer. The printer’s build platform, which is typically a flat plate, is lowered into the resin. The platform is then lifted up slightly, and a light source, usually a UV laser or LED, is directed onto the resin. This causes the resin to solidify, creating the first layer of the print.
The platform is then lowered back into the vat, and a new layer of resin is added on top of the previous layer. The light source is again directed onto the resin, curing the new layer and bonding it to the previous layer. This process is repeated layer by layer until the print is complete.
Types of Resin 3D Printers
There are two types of resin 3D printers: Digital Light Processing (DLP) printers and Stereolithography (SLA) printers. While both types of printers use the same basic technology, there are some key differences between the two.
DLP Printers
DLP printers use a projector to project an image of each layer onto the surface of the resin. The image is created by a digital micromirror device (DMD), which is a chip that contains millions of tiny mirrors. The mirrors can be turned on and off individually, allowing the projector to create an image of each layer.
DLP printers are generally faster than SLA printers, as they can cure an entire layer at once. However, the quality of the print can suffer at the edges of the build platform, as the light from the projector can become distorted.
SLA Printers
SLA printers use a laser to cure the resin, with the laser directed onto the resin using a mirror. The laser can be focused to create very fine details, allowing for highly detailed prints.
SLA printers are generally slower than DLP printers, as the laser has to cure the resin point by point. However, SLA printers can produce higher quality prints than DLP printers, particularly at the edges of the build platform.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Resin 3D Printing
Resin 3D printing offers a number of advantages over other types of 3D printing:
- High level of detail: Resin printers are capable of producing highly detailed, complex designs with a high level of accuracy.
- Smooth finish: Resin prints have a smooth surface finish, which can be sanded and painted to achieve a professional look.
- Wide range of materials: Resin printers can use a wide range of materials, including flexible, transparent, and castable resins.
- Minimal post-processing
Resin 3D printing also has some disadvantages to consider:
- Limited build volume: Resin printers typically have a smaller build volume than FDM printers, limiting the size of the objects that can be printed.
- Messy and hazardous: The liquid resin used in resin printing can be messy and hazardous to handle, requiring proper safety measures and precautions.
- Expensive: Resin printers are generally more expensive than FDM printers, with the cost of resin also being higher than filament.
Applications of Resin 3D Printing
Resin 3D printing has a wide range of applications across various industries. Here are some examples:
- Jewelry making: Resin printing can be used to create highly detailed and intricate jewelry designs.
- Dental and medical: Resin printing can be used to create dental molds, surgical guides, and prosthetics.
- Prototyping: Resin printing is ideal for creating detailed prototypes for product development.
- Architecture and engineering: Resin printing can be used to create detailed architectural and engineering models.
- Art and sculpture: Resin printing can be used to create unique and complex art pieces and sculptures.
Conclusion
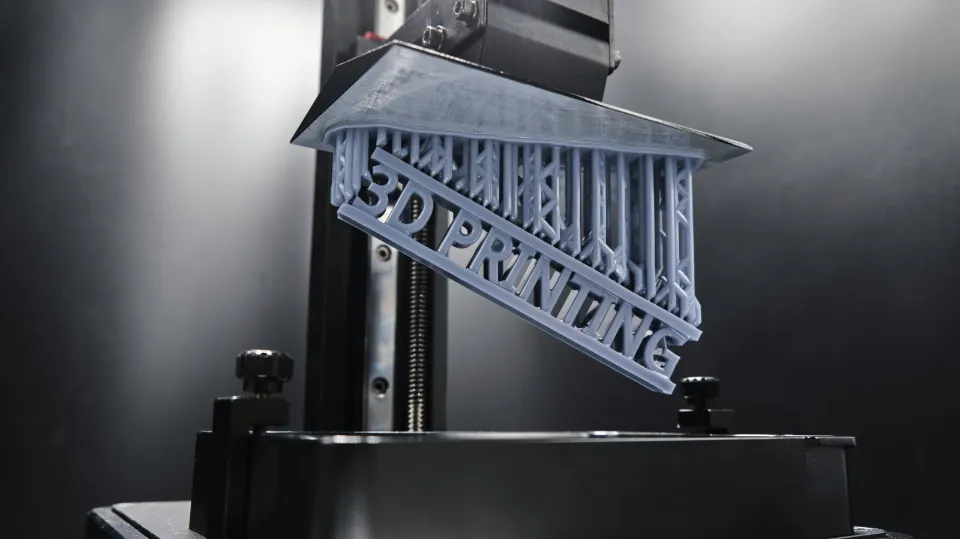

Resin 3D printers are an exciting technology that offer a high level of detail and accuracy, making them ideal for a wide range of applications. While they have some disadvantages to consider, their advantages and applications make them a valuable tool for many industries. Understanding how resin printers work is key to unlocking their full potential and creating high-quality 3D prints.
